Legal Considerations in DFIR
Table of Contents
Introduction to Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR) Link to Introduction to Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR)
Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR) encompasses the systematic process of detecting, investigating, and responding to cybersecurity incidents while ensuring legal integrity. The principles underlying DFIR are vital for effective incident management, legal compliance, and maintaining the trustworthiness of digital evidence.
Key Principles of DFIR Link to Key Principles of DFIR
- Preservation of Evidence: Ensure that digital evidence is maintained in its original state to prevent tampering or alteration.
- Identification and Collection: Quickly identify and collect relevant data from compromised systems while adhering to legal standards.
- Analysis: Conduct a thorough examination of the data to understand the scope and impact of the incident.
- Reporting and Documentation: Document all findings and actions taken during the investigation for accountability and future reference.
Ethical Considerations in Digital Investigations Link to Ethical Considerations in Digital Investigations
Ethical practices are crucial in DFIR to protect the rights of individuals and organizations involved. Investigators must ensure:
- Confidentiality: Safeguarding sensitive information.
- Integrity: Conducting investigations without bias or conflict of interest.
- Transparency: Providing clear and accurate reporting of findings.
Importance of Chain of Custody Link to Importance of Chain of Custody
The Chain of Custody refers to the documented process that tracks the handling of evidence from the moment it is collected until it is presented in court. Its importance includes:
- Legal Admissibility: Maintaining a clear chain helps establish the authenticity of evidence.
- Accountability: Ensures that all individuals involved in the handling of evidence are documented and responsible for their actions.
Legal Standards for Acquiring Forensic Disk Images Link to Legal Standards for Acquiring Forensic Disk Images
Adhering to legal standards during the acquisition of forensic images is essential to ensure their admissibility in court:
- Authorization: Obtain necessary permissions before accessing systems.
- Use of Forensic Tools: Utilize verified and industry-standard tools for imaging to avoid data alteration.
- Documentation: Record the process meticulously, including date, time, and methods used.
Best Practices for Analyzing Digital Evidence Link to Best Practices for Analyzing Digital Evidence
To ensure compliance with legal and regulatory standards during analysis:
- Use Write Blockers: Prevent alteration of data when accessing storage media.
- Maintain Original Evidence: Always work from copies of the data, keeping the original evidence untouched.
- Follow Established Protocols: Adhere to frameworks like the NIST guidelines for digital forensics.
- Engage Legal Counsel: Involve legal advisors during investigations to ensure compliance with laws and regulations.
Room Prerequisites Link to Room Prerequisites
- Incident Response Module: Understanding initial response strategies to security breaches.
- Becoming a First Responder: Training to recognize and assess security incidents swiftly.
Connecting to the Virtual Machine Link to Connecting to the Virtual Machine
To begin the practical aspect of this module:
- Click the green “Start Machine” button in the upper right section.
- If the VM is not visible, select the “Show Split View” button.
- Connect via RDP using provided credentials if necessary.
- Wait approximately 4 minutes for the VM to fully deploy.
- Microsoft Outlook will launch automatically; follow the instructions to bypass activation prompts.
Incident Detection and Initial Response Link to Incident Detection and Initial Response
Incident Scenario Link to Incident Scenario
The Chief Finance Officer (CFO) received an email receipt for an unauthorized transaction over $9,000. Both the CFO and their Executive Assistant (EA) deny making the purchase. The CFO alerted the Human Resources (HR) and Security Operations (SecOps) team to investigate the matter.
Importance of Incident Detection Link to Importance of Incident Detection
Incident detection relies not only on technical controls but also on the involvement of individuals. Responders must remain calm, understand the situation, and gather information from various sources.
Initial Response Link to Initial Response
The initial response is influenced by the incident’s nature and the responder’s experience. It typically involves piecing together evidence and using investigative techniques and tools.
Importance of Documentation Link to Importance of Documentation
Thorough documentation is crucial. Key points to document include:
- Details on persons of interest and their involvement.
- Actions leading to the incident, such as interacting with a phishing site.
- Nature and extent of compromised data.
- Any evidence that sheds light on the incident.
Even if browsing history is missing, other sources like network logs can reveal traces of the incident. It’s essential to note important timestamps:
- The date and time the incident was detected.
- The timeline of events leading to detection.
- Response actions taken after detection.
Understanding the Cause Link to Understanding the Cause
Understanding why the incident happened helps strengthen security. Important aspects include:
- Analyzing how the phishing scam was successful.
- Identifying knowledge or communication gaps.
- Formulating recommendations for policy and training updates.
Documentation and Court Admissibility Link to Documentation and Court Admissibility
Proper documentation ensures that evidence can be presented in court. Clear records strengthen the legal standing of the actions taken. 
Standard Operating Procedures for Communication Link to Standard Operating Procedures for Communication
Establishing communication protocols is vital during an incident. Key points include:
- Utilization of Designated Channels: Use structured approaches for reporting and urgent communications.
- Timely Notification: Inform key stakeholders promptly to initiate coordinated responses.
- Clarity and Consistency: Ensure messages are clear and prevent misinformation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet legal requirements to mitigate potential repercussions.
Incident Response Process Link to Incident Response Process
A robust Incident Response (IR) process is essential for effective communication and management:
- Clear Reporting Path: Inform constituents about the process for reporting concerns.
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Ensure each team member knows their tasks.
- Continual Updates: Regularly update all parties as the situation evolves.
- Post-Incident Review: Effective communication aids in identifying lessons learned.
Reminder Link to Reminder
As you proceed with the tasks, think like an incident responder. Focus on advancing the investigation by following procedures and utilizing your skills. Your decisions should align with the scenario’s objectives. Now, let’s proceed with the investigation.
- What is the Ticket# of the reported incident? in the list of mails look for
NoReply: SupportMe Workflowclick on the mail, in the table look forOTRS ticket Number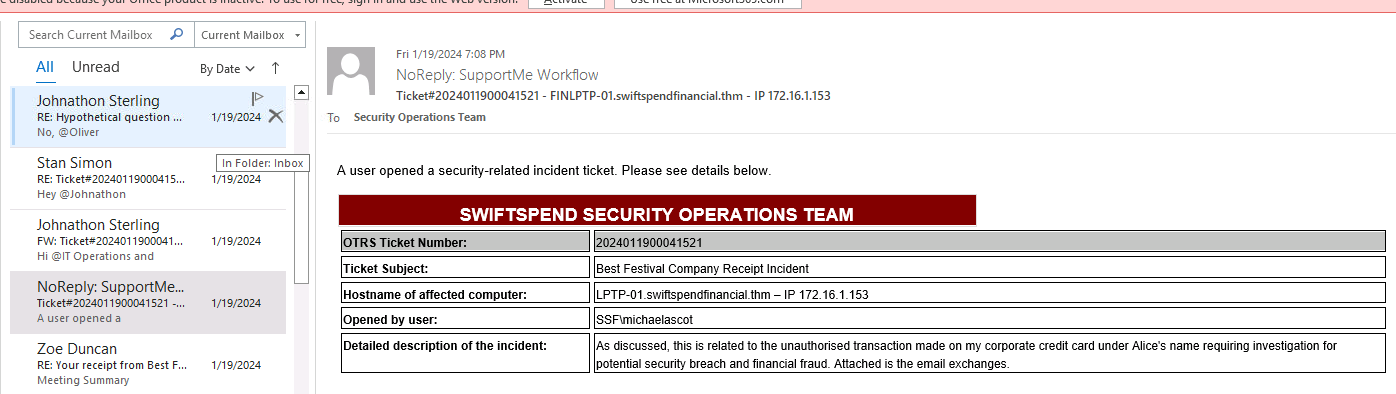
View Answer.
- What is the email of the primary person of interest (POI)?A Person of Interest (POI) in incident response is someone relevant to the investigation of a security incident. They may be directly involved, a witness, or have useful information. Identifying and documenting POIs is crucial, as their insights can help clarify the incident and support prevention strategies and legal actionsto answer this question, i look through the recived mails, and i found one mail give a summary of Participants the role and responsibilities it looks something like this
12345678910111213141516171819Meeting Summary
Participants
- @John
- @Oliver
- @Emily
- @Zoe
- @Michael
- @Alice
Thank you all for attending this meeting on such short notice. Your prompt response and commitment are greatly appreciated under these circumstances.
Key Action Points
- Michael will initiate the process by formally opening a SupportMe Ticket to document and track the issue.
- Oliver is appointed the lead investigator into the unauthorized transaction, with John providing crucial support.
- Alice shared her Outlook OST file with Oliver during the call as requested for a detailed examination of her email activities and potential phishing attempts.
- John will collaborate with Derick's team to secure and analyze relevant logs to identify any signs of a security breach.
- Alice and Michael will jointly review the invoicing platform, scrutinizing it for other suspicious financial activities.
- Emily will oversee the overall investigation and provide regular updates to senior management, ensuring transparency and timely resolution.
so we can clearly see the POI is Alice, and i scrolled down and obtained the mail
View Answer.
- Who is the POI reporting to?
View Answer.
- What specific kind of logs was requested from IT? as we cann see in the image below john is requesting for Exchange IIS server logs
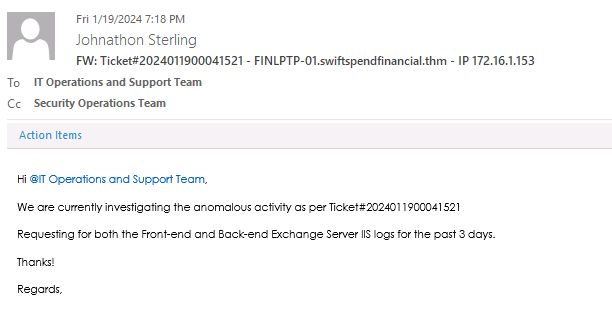
View Answer.
- What is the timestamp of IT’s response to the request for logs? if look at the top of the mail, we can see the timestamp
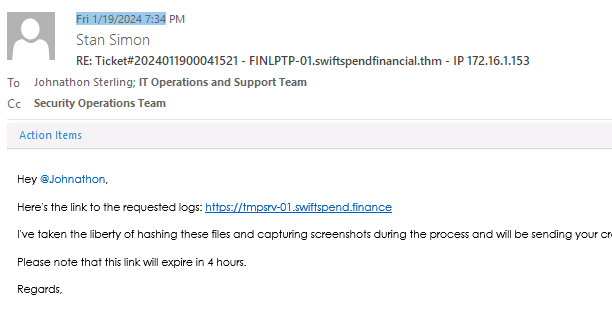
View Answer.
Ethical Decision-Making and Legal Compliance Link to Ethical Decision-Making and Legal Compliance
Evidence-based Approach Link to Evidence-based Approach
Digital forensics practitioners must avoid making hasty conclusions. Viewing a person of interest through a biased lens can compromise the integrity of an investigation. An evidence-based approach ensures thorough investigations that adhere to legal standards, focusing on what the evidence shows and allowing for repeatable, credible conclusions.
Burden of Proof in Digital Forensics Link to Burden of Proof in Digital Forensics
Investigators must provide sufficient, credible evidence to support their findings. The burden of proof ensures that conclusions are legally defensible, requiring adherence to high standards of evidence and ethical guidelines throughout the investigative process.
Ethical Decision-Making Link to Ethical Decision-Making
Ethical decision-making is vital in investigations to prevent illegal or unethical actions. Practitioners must respect privacy and perform only authorized actions during investigations. Ethical issues often arise regarding the handling of personal and sensitive information.
Legal Compliance Link to Legal Compliance
Legal compliance is fundamental in digital forensics, governed by frameworks like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA). These laws impact how digital investigations are conducted, emphasizing the need for an evidence-based approach that respects individual rights while uncovering the truth.
Responsibility of Authority in Digital Investigations Link to Responsibility of Authority in Digital Investigations
Authority figures, including incident responders and law enforcement, hold significant responsibility for maintaining the integrity of investigations. They must set guidelines, provide oversight, and promote a culture of ethical decision-making while staying updated on legal standards.
Understanding Authority Link to Understanding Authority
Recognizing authority in digital investigations is crucial. Legal decisions are ultimately made by judges and lawmakers, highlighting the importance of respecting their interpretations of laws like SOX and CFAA. Incident responders must balance personal ethics with professional conduct and legal compliance to ensure effective investigations.

Using the above pictures to answers the below questions
- Based on email communications, what clause of the Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) email received by the POI did they violate?
View Answer.
-Based on email communications, what anomaly did your colleague suggest looking for within the Front-end and Back-end IIS logs of the Server?
View Answer.
- What is the User-Agent of the anomalous IP address with a successful login attempt?
Legal Considerations in DFIR
© EveSunMaple | CC BY-SA 4.0